What Does it Mean to Have Rh Negative Blood? A Comprehensive Guide
Blood types play a crucial role in various aspects of healthcare, from transfusions to understanding genetic inheritance. The Rh factor is a key component among the different blood type classifications. The Rh factor, whether positive or negative, can have significant health implications, particularly in pregnancy and blood transfusions.
This comprehensive guide aims to shed light on what it means to have Rh negative blood, exploring its characteristics, and health implications, and addressing common myths and facts.
Our goal is to provide accessible and encouraging information to help you understand and manage your Rh status effectively.
Understanding Blood Types
The presence or absence of specific antigens on the surface of red blood cells determines blood types. The ABO blood group system is the most well-known classification, categorizing blood into four main types: A, B, AB, and O. Each blood type differs based on the antigens—A and B proteins—found on the cell’s surface. For example, type A blood has the A antigen, type B has the B antigen, type AB has both, and type O has neither.
Understanding your blood type is critically important in healthcare, particularly for safe blood transfusions. Mismatched blood types can lead to serious and potentially life-threatening reactions.
In addition to transfusions, knowing your blood type can be vital during surgeries, organ transplants, and pregnancy, where incompatibility issues might arise. Therefore, awareness and knowledge of blood types are essential for effective medical care and emergency preparedness.
What is the Rh Factor?
The Rh factor, an essential component in blood typing, refers to the presence or absence of the Rhesus (Rh) antigen on the surface of red blood cells. If your blood cells have this protein, you are Rh positive; if not, you are Rh negative.
The history of the Rh factor dates back to 1937 when Dr. Karl Landsteiner and Dr. Alexander S. Wiener discovered it during research on Rhesus monkeys. Their groundbreaking work not only expanded the understanding of human blood types but also cemented the critical role of the Rh factor in transfusion medicine and prenatal care.
This discovery highlighted the significance of the Rh protein in preventing hemolytic disease in the newborn and ensuring compatible blood transfusions, underscoring the importance of knowing one’s Rh status.
Rh Negative Blood Explained
Rh negative blood is defined by the absence of the Rh antigen, a protein found on the surface of red blood cells. While the presence of the Rh factor (Rh positive) is far more common—occurring in about 85% of the population—roughly 15% of people are Rh negative.
This difference means that Rh negative blood cells do not have the Rh antigen, and this can influence various aspects of health, particularly in medical situations such as pregnancies and blood transfusions. The primary distinction between Rh positive and Rh negative blood lies in this specific protein: its presence in Rh positive individuals and absence in Rh negative ones.
Despite being less common, Rh negative blood plays a critical role in transfusion medicine, especially for patients who are also Rh negative and can only safely receive Rh negative blood. Understanding this distinction and the prevalence of Rh negative blood is crucial for effective medical care and emergency preparedness.
Health Implications of Rh Negative Blood
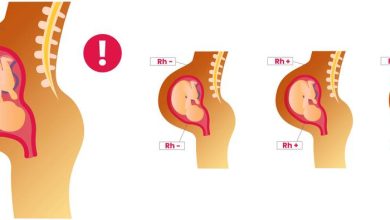
The health implications of having Rh negative blood are particularly significant during pregnancy, where Rh incompatibility can pose serious risks and complications.
Rh incompatibility occurs when an Rh negative mother carries an Rh positive fetus, potentially leading to hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN), where the mother’s immune system attacks the baby’s red blood cells. This can result in severe anemia, jaundice, and even heart failure for the infant if left untreated.
Preventative measures such as the administration of Rh immunoglobulin (RhoGAM) during and after pregnancy can mitigate these risks by preventing the mother’s immune response to Rh positive cells. Understanding one’s Rh status is crucial, as it allows for prompt and effective management of these potential complications, ensuring both maternal and infant health are safeguarded.
Myths and Facts About Rh Negative Blood
When it comes to Rh negative blood, several myths and misconceptions tend to circulate, often overshadowing the scientifically supported facts.
One common misconception is that individuals with Rh negative blood possess unique or supernatural traits, which is not substantiated by scientific evidence.
Another myth suggests that Rh negative blood is prone to more health problems, whereas, in reality, the primary medical concerns related to Rh negative blood involve pregnancy and blood transfusions, specifically Rh incompatibility. Scientifically supported facts emphasize the genetic basis of the Rh factor and its inheritance patterns.
Additionally, it is crucial to understand that the absence of the Rh antigen does not impact overall health or immune function outside specific medical circumstances. By distinguishing between myths and facts, individuals can better navigate their Rh status with accurate knowledge and less anxiety.
Rh Negative Blood and Blood Donations
Blood donations from Rh negative individuals are particularly valuable because of their unique compatibility requirements. In transfusion medicine, compatibility is crucial; an Rh negative patient can only receive Rh negative blood to avoid adverse reactions. This makes Rh negative donors incredibly important, especially since Rh negative blood is less common. Their contributions ensure a safe and reliable supply for patients in urgent need of compatible blood.
By donating, Rh negative individuals help to fill a critical gap, supporting lifesaving medical procedures and emergency care. Every donation from an Rh negative donor is a lifeline, reinforcing the importance of regular blood donations to maintain a robust and ready supply for those whose health relies on this specific need.
Living with Rh Negative Blood
Living with Rh negative blood may come with unique healthcare considerations, but effective management ensures a healthy and worry-free life. Regular check-ups and open communication with your healthcare provider are crucial. If you’re planning a pregnancy or require a transfusion, informing your medical team about your Rh status can preempt potential complications.
Staying aware of your Rh negative status allows for timely preventative measures, such as receiving Rh immunoglobulin during pregnancy to prevent hemolytic disease in the newborn. Emphasizing the importance of regular health check-ups, individuals with Rh negative blood can proactively manage their health and navigate medical treatments with greater confidence and safety.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding what it means to have Rh negative blood is essential for effective medical care and personal health management. We’ve explored the origins of the Rh factor, the characteristics of Rh negative blood, and the critical medical implications, particularly during pregnancy and blood transfusions. Dispelling myths and recognizing the facts about Rh negative blood equips individuals with accurate knowledge, helping to navigate potential health concerns with confidence.
We encourage you to continue learning about your Rh status and to share this information with others, fostering greater awareness and preparedness within your community. Your efforts in staying informed and guiding others can make a tangible difference, ensuring that everyone benefits from a deeper understanding of Rh negative blood.
Additional Resources and Further Reading
Credible Healthcare Sites and Resources
American Red Cross: An important resource for information on blood donations, particularly for those with Rh negative blood. Visit American Red Cross
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): Provides comprehensive information on various health topics, including prenatal care and Rh incompatibility. Visit CDC
National Institutes of Health (NIH): Offers in-depth research articles and updates on Rh negative blood and related health implications. Visit NIH
American Association of Blood Banks (AABB): An excellent source for information on blood banking and transfusion medicine. Visit AABB Recommendations for Further Reading