Rh Negative Blood and Pregnancy: What You Need to Know
When it comes to pregnancy, understanding your blood type can be crucial, especially if you have Rh negative blood. The Rh factor is a specific protein found on the surface of red blood cells, and its presence or absence can significantly impact your pregnancy journey.
For those with Rh negative blood, knowing how this factor interacts with Rh positive blood is essential in preventing potential complications. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of Rh negative blood and its importance in pregnancy, equipping expectant mothers with the knowledge they need to ensure a healthy and safe experience.
What is Rh Negative Blood?
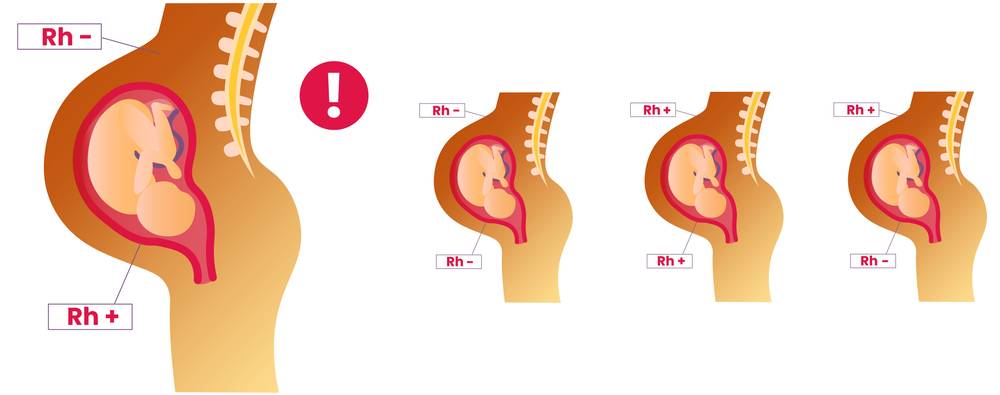
The Rh factor is a protein that can be present on the surface of red blood cells. Individuals who have this protein are classified as Rh positive, while those who lack the protein are termed Rh negative. The differentiation between Rh positive and Rh negative blood is significant in medical contexts, especially during pregnancy, because it can affect the interaction between a mother’s blood and that of her baby.
If an Rh negative mother carries an Rh positive baby, her body might recognize the baby’s Rh positive blood cells as foreign, potentially leading to complications if not properly managed. Understanding whether you are Rh positive or Rh negative is, therefore, a crucial step in prenatal care.
The Importance of Rh Factor in Pregnancy
Determining Rh factor compatibility is a vital part of prenatal care, as mismatched Rh factors between a mother and her baby can lead to serious complications. During an initial prenatal visit, blood tests are conducted to ascertain the Rh status of both the mother and the father.
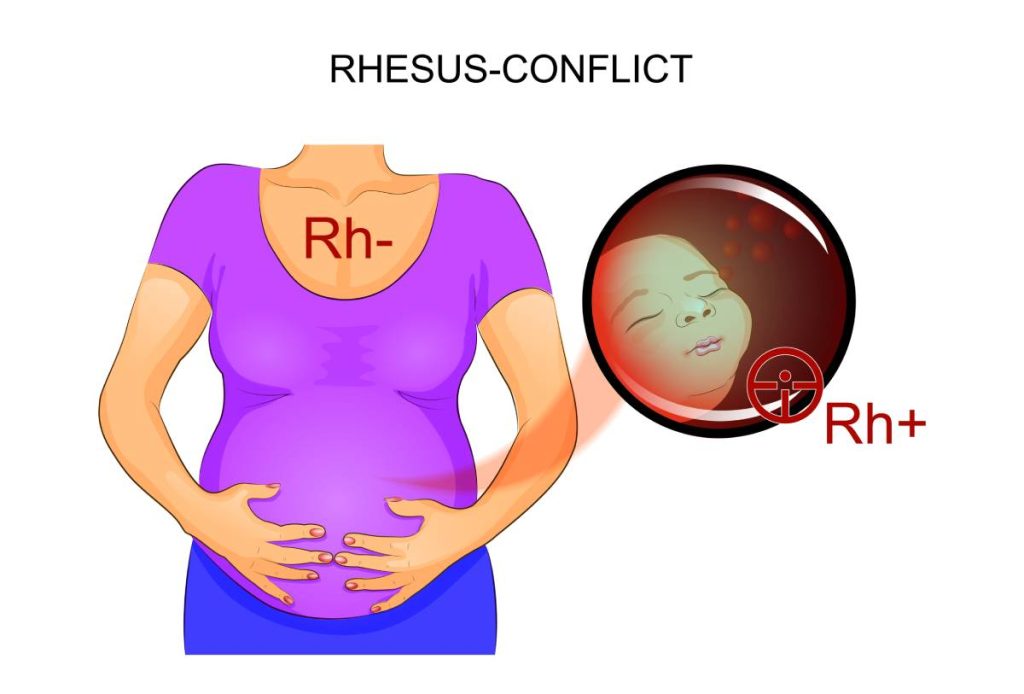
If the mother is Rh negative and the father is Rh positive, there’s a possibility that the baby could inherit the Rh positive trait. In such cases, the mother’s immune system might treat the baby’s Rh positive red blood cells as foreign invaders, potentially leading to Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn (HDN), where the baby’s red blood cells are destroyed.
This can result in anemia, jaundice, heart failure, or even stillbirth if not properly addressed. Therefore, recognizing and managing Rh incompatibility is crucial to ensure the health and safety of both the mother and the baby throughout the pregnancy.
Rh Incompatibility: Risks and Concerns
One of the primary risks associated with Rh incompatibility is Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn (HDN). This condition arises when an Rh negative mother develops antibodies that attack the Rh positive red blood cells of her baby. The destruction of these red blood cells can lead to a range of serious symptoms and potential effects on the baby.
Among the immediate concerns are anemia and jaundice, which result from the rapid breakdown of blood cells. Anemia can deprive the baby’s organs of essential oxygen, while jaundice, characterized by yellowing of the skin and eyes, indicates an excess of bilirubin—a byproduct of red blood cell breakdown. In severe cases, HDN can escalate to heart failure or hydrops fetalis, a life-threatening condition where abnormal amounts of fluid build up in the baby’s tissues and organs.
Without timely intervention, these complications can, unfortunately, lead to stillbirth or neonatal death. Therefore, understanding and addressing Rh incompatibility is critical to mitigating these risks and ensuring the wellbeing of both mother and baby.
Diagnosis and Testing
The diagnosis and testing of Rh factor during pregnancy are pivotal steps in ensuring maternal and fetal health. Prenatal blood tests, typically conducted during the first trimester, are designed to determine the Rh factor of both the mother and the baby.
If the mother is found to be Rh negative, additional blood tests may be performed throughout the pregnancy to monitor any potential development of antibodies against Rh positive blood cells. These tests help to assess the risk of Rh incompatibility and guide the necessary preventive measures. The frequency and types of testing can vary based on the pregnancy’s progression and the presence of any complications.
Regular prenatal visits are essential for ongoing evaluation and management, ensuring that any issues related to Rh incompatibility are promptly addressed to safeguard the health of both the mother and the baby.
Preventative Measures and Treatments
To mitigate the risks associated with Rh incompatibility, administering Rh immunoglobulin (RhIg) shots is a crucial preventive measure. RhIg, also known as Rho(D) immune globulin, works by preventing the mother’s immune system from producing antibodies against Rh positive red blood cells. The standard protocol involves administering a RhIg shot around the 28th week of pregnancy and another within 72 hours after delivery if the baby is Rh positive.
Additionally, if any events during the pregnancy might lead to blood mixing, such as amniocentesis, chorionic villus sampling (CVS), or any trauma to the abdomen, an extra dose of RhIg may be required. Alongside RhIg, continuous monitoring through regular prenatal care is essential. This includes routine blood tests to track the presence of antibodies and ensure that any signs of Rh sensitization are detected early.
In cases where sensitization occurs, further medical interventions, such as intrauterine transfusions or early delivery, might be necessary to protect the baby. Comprehensive monitoring and timely administration of RhIg are key to managing Rh incompatibility effectively.
Living with Rh Negative Blood During Pregnancy
Living with Rh negative blood during pregnancy can be a source of anxiety and stress for expectant mothers, especially with the potential complications associated with Rh incompatibility. However, managing these emotions is essential for both maternal and fetal health. Stress-reduction techniques such as prenatal yoga, meditation, and joining support groups with other Rh negative mothers can be beneficial.
Moreover, the importance of regular prenatal care and follow-ups cannot be stressed enough. Consistent appointments with healthcare providers ensure that any concerns are promptly addressed and that preventative measures, like Rh immunoglobulin (RhIg) shots, are administered on schedule. Early and frequent monitoring allows for timely interventions, significantly reducing the risks associated with Rh incompatibility.
By staying informed, maintaining open communication with medical professionals, and following through with recommended prenatal care, mothers with Rh negative blood can navigate their pregnancies more confidently and ensure the wellbeing of their babies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding Rh negative blood during pregnancy and the associated risks of Rh incompatibility is critical for ensuring both maternal and fetal health. We’ve highlighted the importance of early diagnosis and testing, preventive measures like the administration of Rh immunoglobulin shots, and the necessity of continuous monitoring through regular prenatal care.
Furthermore, managing the emotional and physical aspects of pregnancy with Rh negative blood is achievable through stress-reduction techniques and support systems. Remember, open dialogues with your healthcare providers are essential for tailoring the best care plan for you and your baby.
By staying informed and proactive, mothers with Rh negative blood can navigate their pregnancies with confidence and ensure the wellbeing of their little ones.
Further Resources and Recommended Readings
Reputable Sources
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG): ACOG provides extensive resources on Rh incompatibility and guidelines for pregnant women with Rh negative blood. Visit ACOG’s website
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): The CDC offers valuable information on Rh disease, prevention strategies, and treatment options. Visit the CDC’s website
BabyCenter Community: Join discussions with other expectant mothers experiencing similar concerns regarding Rh incompatibility. Visit BabyCenter Community
March of Dimes: Provides support and resources for women with Rh negative blood and other prenatal concerns. Visit March of Dimes
What to Expect Community: Connect with other parents-to-be and share experiences, questions, and advice. Visit What to Expect Community Recommended Readings“What to Expect When You’re Expecting” by Heidi Murkoff and Sharon Mazel: This comprehensive guide covers all aspects of pregnancy, including managing Rh negative blood.
“The Rh Factor: How It Can Affect Your Pregnancy” by Jack Salmon: Offers detailed insights into Rh incompatibility and practical advice for expectant mothers.
“Pregnancy Day by Day” by DK: Features daily updates on fetal development and health tips, including dealing with Rh related issues. These resources and readings can provide vital information and support, helping mothers with Rh negative blood navigate their pregnancies with confidence and peace of mind.